Activation of Macrophages Is Best Achoeved by Which Cytokine
T cell activation begins when a T cell is ingested by a macrophage C T cell activation begins with a cell processing and displaying antigen fragments on its MHC molecules. Its main activities concern the suppression of macrophage activation and production of TNF IL-1β IL-6 IL-8 IL-12 and GM-CSF.

Macrophage Polarization Assays Promab
Impermeable Transport blood.
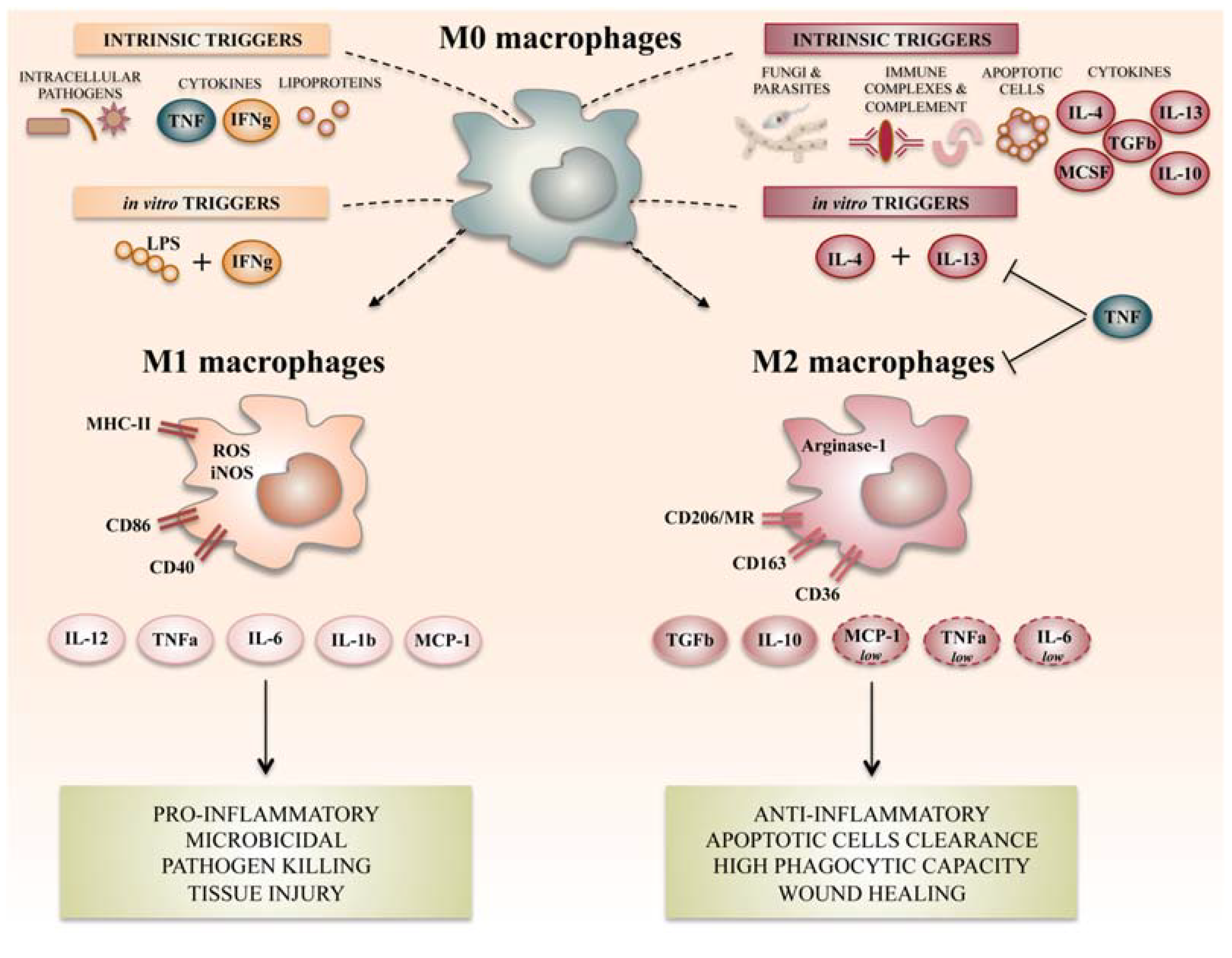
. Inflammation is tightly regulated by multiple inhibitors and antagonists. Activated T helper Th cells secrete IFN-gamma which activate macrophages to secrete IL-2 which then activates Th cells to produce other cytokines. In concert with other mediators cytokines bias the fate of macrophages into a spectrum of inflammation-promoting classically activated to anti-inflammatory or alternatively activated macrophages.
A portfolio of cytokines is central to the role of macrophages as sentries of the innate immune system that mediate the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Cytokine secreted by a specific type of cell can activate target cell to produce additional cytokines -ex. Macrophage activation syndrome MAS is an episode of overwhelming inflammation that occurs most commonly in children with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis SJIA.
Macrophage activation is a complex process involving coordinatesynergistic action of signals from cytokines chemokines and PAMPs44 IFN-γ is the most potent macrophage-activating factor inducing inflammatory macrophages called M1 45 Full macrophage activation requires previous priming that may be provided by low levels of IFNs. Most of these are mediated by cytokines and antigens present on microbes. A macrophage-activating factor is a lymphokine or other receptor based signal that primes macrophages towards cytotoxicity to tumors cytokine secretion or clearance of pathogens.
Macrophage activation syndrome and cytokine-directed therapies. IL-10 is a 35 kD cytokine identified in 1989 and is produced by activated macrophages B cells and T cells. What best describes lymphatic capillaries.
Macrophage activation is dependent on receptors which in turn respond to a variety of external signals. It is produced largely by monocytes and macrophages that are activated by toll-like receptor ligands such as endotoxin as well as cytokines such as IL-18 and stimulates local endothelial cells as well as lymphocytes. It is present as an inactive form pro-IL-1β.
However upon activation of cells it is cleaved by caspase-1 to the biologically active form. A MAF can also alter the ability of macrophages to present MHC I antigen participate in Th responses andor. It is characterized by expansion and activation of T lymphocytes and hemophagocytic macrophages and bears great similarity to.
IL-1β is a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced primarily by monocytes and macrophages. Cancer cells can suppress T cell activity by releasing __. Similar molecules may cause development of an inhibitory regulatory phenotype.

Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Human Macrophage Polarization In Inflammation During Infectious Diseases Html
Targeting Macrophages In Cancer Immunotherapy Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy

Macrophage Polarization Exposure To Different Cytokine Milieu Promotes Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Activation of Macrophages Is Best Achoeved by Which Cytokine"
Post a Comment